Microsoft has released a tutorial on how to stop the $35 credit card-sized Raspberry Pi computer from overheating.
Ofer Dekel, principal researcher at Microsoft, says the latest version of the Pi, the Raspberry Pi 3 Model B, “tends to overheat when pushed to its limits”.
When using the Pi 3 to run a “compute-intensive AI model” he noticed it would heat to the point where board would begin to throttle its performance or even shut down to prevent damage.
He posted infra-red images, displayed below, which show the Pi heating up to 91.7C when running the AI model, past the ~80C threshold where the board starts to reduce the clock speed of its processor.
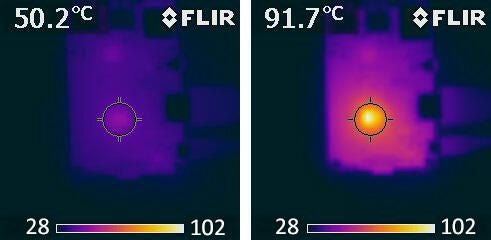
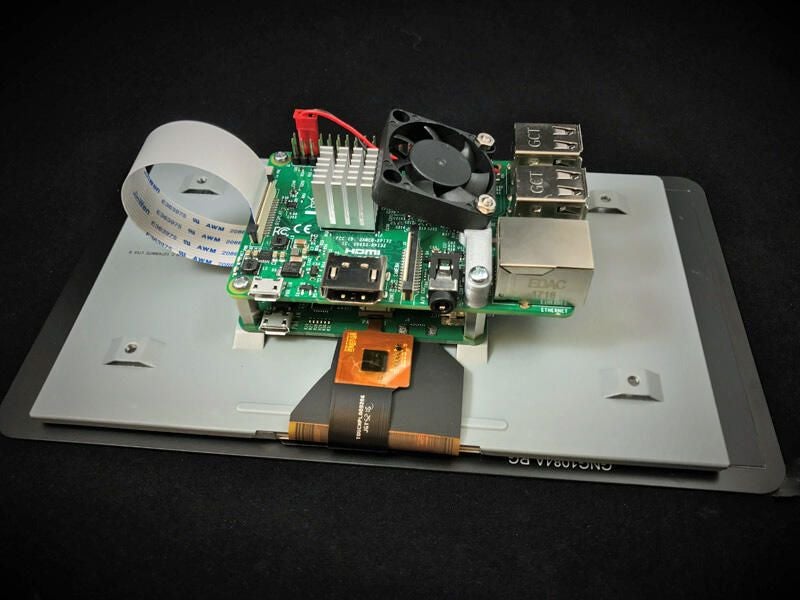
To address this problem, Dekel put together a step-by-step guide to cooling the Pi 3, outlining how to attach a heatsink and a fan to the processor.
SEE: Hardware spotlight: The Raspberry Pi
The makeshift cooling solution is composed of parts costing about $5, most of which are available from the site Adafruit. The most challenging part to source for those who don’t own a 3D printer will be the 3D-printed Pi 3 Fan Mount, where using a print-on-demand service such as Shapeways may be necessary.
Using just a heatsink to cool the Pi is “insufficient”, according to Dekel, who produced the graph below, showing the temperature of the board when running all four cores at 100% for 12 minutes.
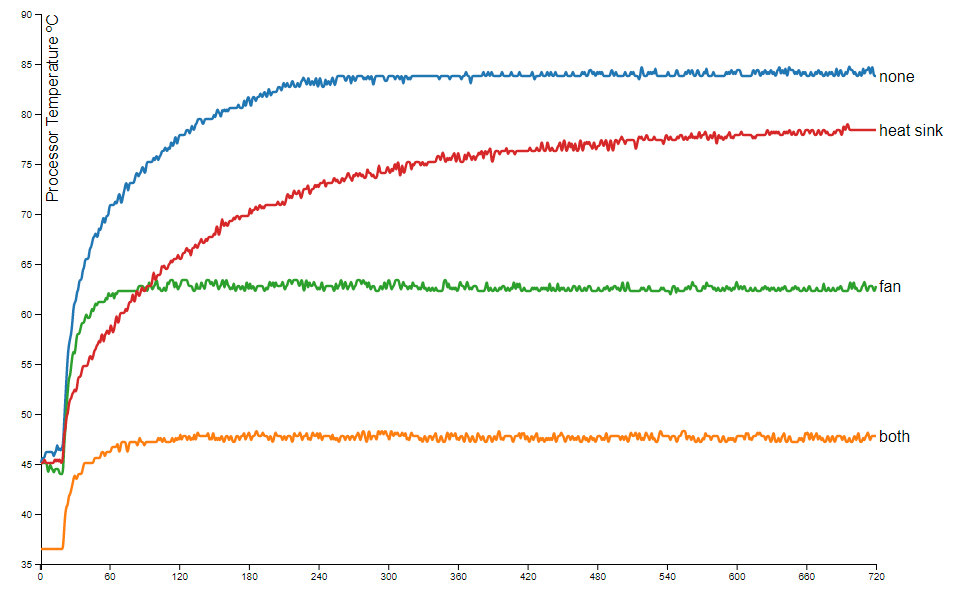
“The combination of fan and heat sink works like a champion, and the processor temperature remains below 50 degrees,” he said.
There were reports of the Pi 3 overheating around the time of the board’s release in 2016, with some saying the board reached close to 100C after five minutes at 100% load.
At the time, the co-creator of the board Eben Upton said that–outside of synthetic tests that place the board’s processor under prolonged strain–the Pi 3 was highly unlikely to see temperatures rise that high.
When not under load, the Pi’s CPU operates at 600MHz, increasing its speed to 1.2GHz when tasked with carrying out a heavyweight operation. Operating at this higher speed will begin to raise the temperature of the board and when it goes over ~80C the Pi 3 will start to reduce its operating frequency in order to reduce the heat emitted by the CPU. Its speed is gradually reduced, dropping down to 600MHz if the board hits 85C or over.
Microsoft’s Dekel focuses on running machine learning algorithms and technologies on tiny resource-constrained computers such as the Pi, as part of the firm’s edge computing project.
Various attempts are being made to use the Pi to run machine-learning models, with Intel recently releasing its Movidius Neural Compute Stick to boost the rate at which the Pi can carry out vision-related tasks like facial and object recognition.

Read more about the Raspberry Pi
- Raspberry Pi: The smart person’s guide
- Want a more powerful Raspberry Pi? Choose from these 20 alternatives
- GCHQ builds monster Raspberry Pi cloud with OctaPi formation (ZDNet)
- How to give your Raspberry Pi ‘state-of-the art computer vision’ using Intel’s Neural Compute Stick
- Raspberry Pi 3: The inside story from the new $35 computer’s creator
- Raspberry Pi in 2017: New boards, new OSes and more
- Choosing a Raspberry Pi OS? Here’s the definitive list
- Raspberry Pi rival delivers a 4K Android computer for just $25
- Raspberry Pi and Docker: Tiny $35 computer gets major new release of HypriotOS (ZDNet)
- Turn any hard drive into networked storage with Raspberry Pi (CNET)