
Most Google Meet sessions work well. You join a session, share your video and remember to unmute your microphone when you speak—and mute it again to convey silence. Breakout rooms, polls, Q&A, screen sharing and collaborative Jamboard sessions all work smoothly.
Sometimes, though, a Google Meet session may be less than optimal. A slow internet connection causes low-resolution video to display or even revert to audio-only. An attempt to share a screen fails. An internet connection drops and disconnects a participant. None of these issues should be considered normal.
SEE: Feature comparison: Time tracking software and systems (TechRepublic Premium)
You may solve some Meet video conferencing challenges quickly. Reboot your modem, router or device (i.e., phone, tablet or computer). If you use a mobile device, move to an area with a stronger signal. Or change connections entirely: Try a cellular network or different Wi-Fi network. If you have access to a faster, more powerful device, give that a try the next time you use Google Meet.
But if you use Google Meet as part of an organization that uses Google Workspace and experience consistent conferencing challenges, let your Google Workspace administrator know. A Google Workspace administrator may access the Meet quality tool to review all sorts of details about a Google Meet session. The details, and a few potential implications of the information, are covered below.
How to assess Google Meet performance by meetings, people and Meet devices
To access the Meet quality tool, a Google Workspace administrator may sign in to the Admin console, then navigate to Apps | Google Workspace | Google Meet | Meet quality tool. This report displays recent Meet sessions held by people within the organization.
The Meet quality tool groups meeting performance data by Meetings (Figure A, circled), Participants or Google Meet devices. These groupings allow an administrator to determine whether a specific session, person or device experiences problems consistently. The different views might point to, for example, issues with a particular person’s equipment or connection, or challenges with a Google Meet device in a conference room. In some cases, a bit of research might confirm that meetings simply encountered problems on a day when there was some sort of significant internet outage.
Figure A
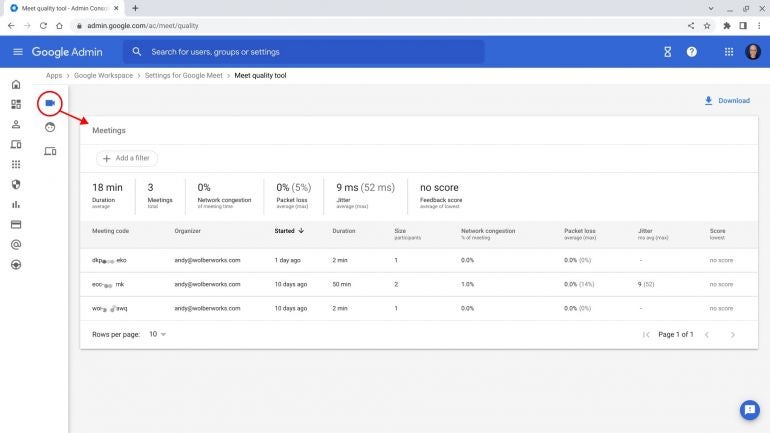
When you have the Meetings option selected, the overall performance information displays in a summary line above the list of individual Meet sessions. This summary includes the number of meetings, average duration, network congestion, packet loss, jitter and any feedback scores. The feedback score is the star rating (on a scale of one to five stars, with five being the best) that participants are prompted to provide at the end of each session. Typically, I suggest you select (click on or tap) the Network congestion column so that session data is sorted from most congested to least (i.e., the arrow to the right of the column title points downward).
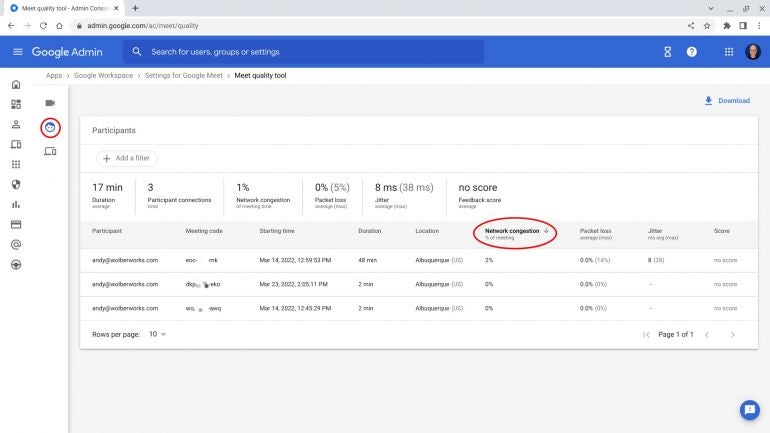
When you have the Participants option selected (Figure B, circled on the left), again a similar set of performance information displays. I suggest you select the Network congestion column (Figure B, oval on the right) to display most congested to least. On this screen, the location of participants also may provide a troubleshooting clue. Consistent network congestion in a location might prompt additional connectivity testing or troubleshooting. Alternatively, location information might also highlight that someone simply had a poor connection on a rarely used network, such as at a hotel or in transit.
Figure B
How to review detailed Meet session data
A Google Workspace administrator also may investigate individual Meet session data. From any of the Meet quality tool lists of sessions, click (or tap) on a row to access meeting details including participants and activities along with network and system, audio, video, and screen share performance, as shown in Figure C. The data lets you review performance throughout the course of a meeting: Who joined (or left) the meeting? What happened to performance when a participant initiated a screen share? How was the audio and video throughout the course of the session?
Figure C
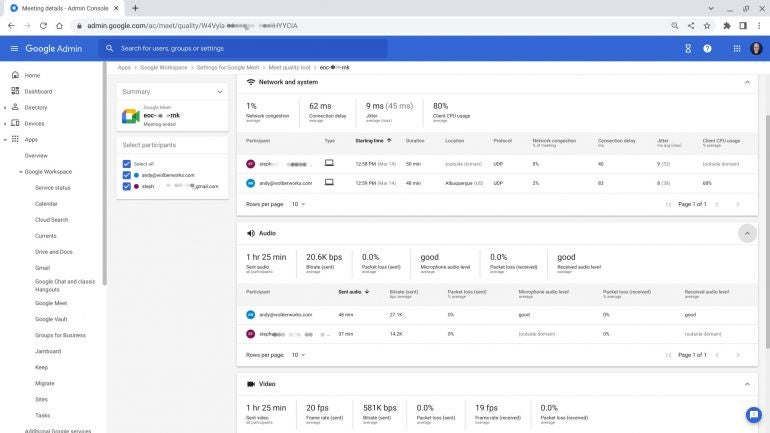
The session data can help you solve Meet conferencing problems:
- Significant network congestion, packet loss or jitter? Try to minimize the load on the local network. If working from home, see what happens if other people stay off the internet while you meet. Or consider upgrades to networking equipment (better Wi-Fi equipment), connections (new cables) or service plans.
- Client CPU usage high? Try to minimize the load on the computer. Test how well things work if you quit every program that isn’t essential before starting a Google Meet session to minimize the load on your system. Close all Chrome tabs that aren’t needed during the meeting.
- Microphone audio level low? Move closer to the microphone, if possible. Or experiment with a different microphone: Try a wired headset, instead of wireless earbuds or a device’s built-in mic.
Remember, there will always be some variability in performance, since so many people connect to Google Meet from various places and with a wide range of devices. Use the Meet quality tool session data to diagnose consistent, recurring patterns and then experiment with potential solutions.
What has your experience been with the Google Meet quality tool?
If you use Google Meet as part of an organization, have you experienced any challenges? If you’re a Google Workspace administrator, how do you use the Meet quality tool to assess performance and address issues? What has been the most interesting conferencing or connection issue you’ve successfully solved? Let me know, either in the comments below or on Twitter (@awolber).
