As more and more of the global workforce have become reliant on home-based network communications equipment like routers and modems, it has also become much more important that the equipment be fined tuned for maximum performance. Even though so many are working remotely these days, it doesn’t change the maxim that “time is money.”
Depending on make, model, sophistication, and age, your home router/modem may be configured for basic web surfing but not for the high-performance exchange of large files, for example. Changing the maximum transfer unit (MTU) setting on your router may boost your overall network speed performance significantly. However, choosing the wrong setting could cripple your router and crush your overall network speeds to a level that is unbearable.
This how-to tutorial shows you how to find the optimum MTU setting for your router and your home network running Microsoft Windows 10 and then shows you how to change that MTU setting to raise network performance.
SEE: Telecommuting policy (TechRepublic Premium)
How to optimize the MTU setting on your router
A caveat to this technique to consider before making any setting changes: If your router is relatively new and technologically superior, it may have features that will adjust the MTU size to self-optimize network activity. This means that forcing a specific and constant MTU on your router may not be necessary, and in fact, harmful to overall performance. Running broadband speed tests to compare results for different MTU settings is recommended.
SEE: How to diagnose and fix Wi-Fi network problems using a Windows 10 PC (TechRepublic)
That being said, let’s move on to finding the optimum MTU value.
The simplest way to establish the optimum MTU is by using the ping command and iterating the MTU setting. In Windows 10, start by right clicking the Start button and selecting the Command (Admin) or Windows PowerShell (Admin) item from the context menu. This opens the system command prompt screen, as shown in Figure A.
Figure A

The maximum MTU size for any IPv4 Ethernet or Wi-Fi connection is 1500. To ping that MTU, use this command:
ping techrepublic.com -f -l 1500
Note: You can use any website. As you can see an MTU setting of 1500 returns a message that says the package needs to be fragmented. In other words, the data packet of 1500 was too large to read. We will have to iterate by reducing the 1500 to a lower number. An MTU of 1492 is standard for PPoE v2, so let’s try that next.
SEE: Why is my internet so slow? (TechRepublic)
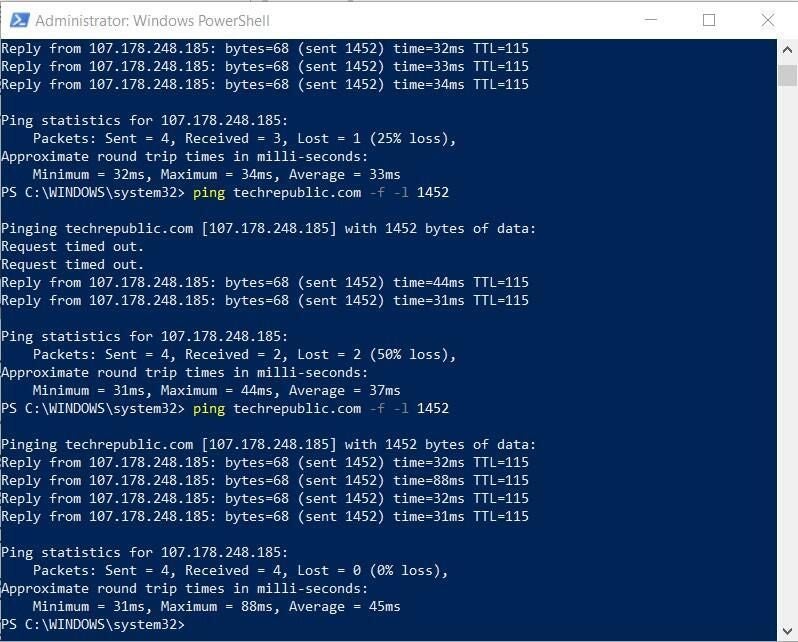
Still too high, so lets try 1452, which is standard for DS-Lite over PPPoE. As you can see in Figure B, we are getting valid pings using 1452.
Figure B
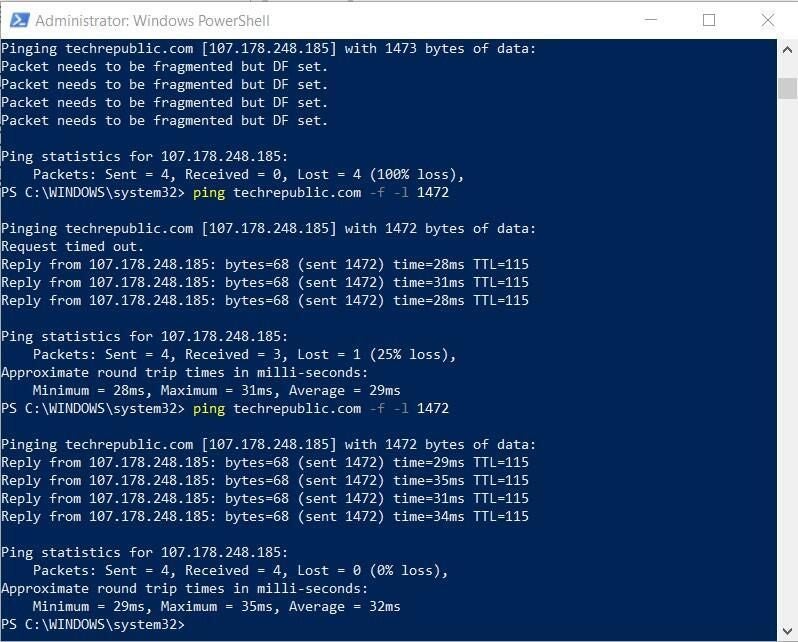
Next, add 10 and try a ping with 1462. If that works, try 1472. Then try 1482. Eventually, you will home in on the maximum size you can set before you get the “data needs to be fragmented” message, which in my case was 1472, as shown in Figure C.
Figure C
Now, that you have a number to work with, you will need to access your router’s settings. For most home routers, access to settings requires a web browser pointing to a specific IP address, such as 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1, etc. This address and the initial username and password should be written on your router or in the documentation that accompanied it.
As an aside, change the default username and password to a combination unique to you ASAP. DO NOT LEAVE THE DEFAULTS.
SEE: Best Wi-Fi router in 2021 (ZDNet)
Each router has different software, so we cannot tell you specifically how to change the MTU on your router, but the setting is typically under Advanced Settings or a similar item in the menu of configuration screens.
When you find the MTU settings screen, change it to the maximum MTU size you pinged earlier and test if your download and upload speeds improve. If they don’t, back down the number until they do. When you are satisfied, close out of your router’s configuration software, saving the settings you have entered.
As mentioned before, changing the MTU setting may not be necessary on some modern routers because the software adjusts the MTU on the fly depending on what it determines is the most efficient setting. For example, as you can see in Figure D, Windows 10 on my system has set the MTU at 1500 for all my network adapters.
Figure D

This high setting allows for maximum head room for each adapter and allows the router to determine optimum setting for data transmission. Specifying an MTU setting in my router/modem configuration is not going to be helpful. Consider your optimization choices carefully.
